How to clear the DNS cache on your computer?
-
 Castor
Castor - 10 Sep, 2023
At times, it’s essential to refresh the DNS cache on your computer, especially during website development or setup. This guide will walk you through the steps for clearing your DNS cache on various various operating systems and web browsers.
Introduction
When you use your computer, it saves DNS information about websites you visit to make them load faster in the future. This usually helps speed up your internet experience. But if you’re building a website or changing website settings, this stored information can sometimes cause problems. It might prevent you from seeing the latest changes you made to your site or even block you from accessing the right websites.
In order to refresh or clear your DNS cache, you should follow the specific steps that correspond to your computer’s operating system or web browser. This essential process ensures that your computer or browser doesn’t rely on outdated information when accessing websites. By refreshing the DNS cache, you enable your system to fetch the most up-to-date and accurate data from the internet, enhancing your overall online experience.
To delve further into this, let’s explore the steps needed to clear the DNS cache for various operating systems and web browsers, ensuring you have the information you require to maintain a smooth and uninterrupted web experience.
Windows operating systems
To clear the DNS cache on Microsoft Windows, follow these steps:
- Open a DOS command window. To do this, click Start, Search for cmd, and then open it.
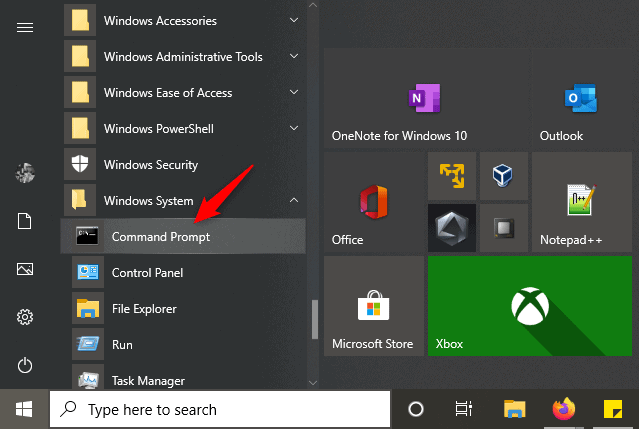
- It will open a command prompt window in Windows OS.
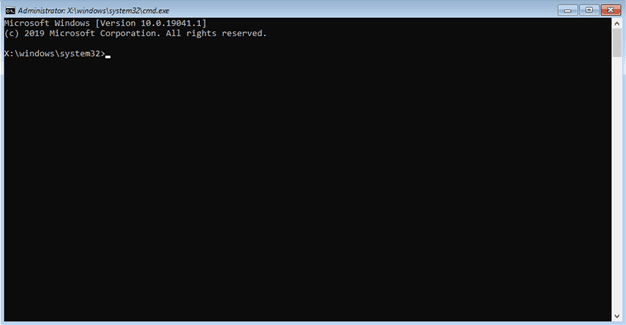
- At the command prompt, type the following command and then press Enter:
ipconfig /flushdns
- Restart your computer.
- The DNS cache is now clear.
Mac OS X operating systems
To clear the DNS cache on Apple Mac OS X, follow these steps:
- Open a terminal window. To do this, click Applications, click Utilities, and then click Terminal.
- At the command prompt, type the appropriate command for your Mac OS X version to clear the cache:
- For OS X Yosemite v10.10.4 or later, type the following command:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder- For OS X Yosemite v10.10 through v10.10.3, type the following command:
sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache- For OS X Mavericks, Mountain Lion, and Lion, type the following command:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder- For Mac OS X Snow Leopard, type the following command:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache - Restart your computer.
- The DNS cache is now clear.
Linux operating systems
Unlike Windows and Mac computers, Linux systems don’t have a DNS cache by default. However, each distribution might use a different DNS service to store DNS records locally. Depending on the service, you can either clear the cache or restart the service.
- Open a terminal window. To do this, click Applications, click Utilities, and then click Terminal.
- In the Terminal window, type in the one of the following commands to find the DNS resolver your system uses.
sudo lsof -i :53 -S
The command will output all services listening to port 53 – the server port reserved for DNS. This way, you can see which is the DNS resolver your Linux is using in order to clear its DNS cache.
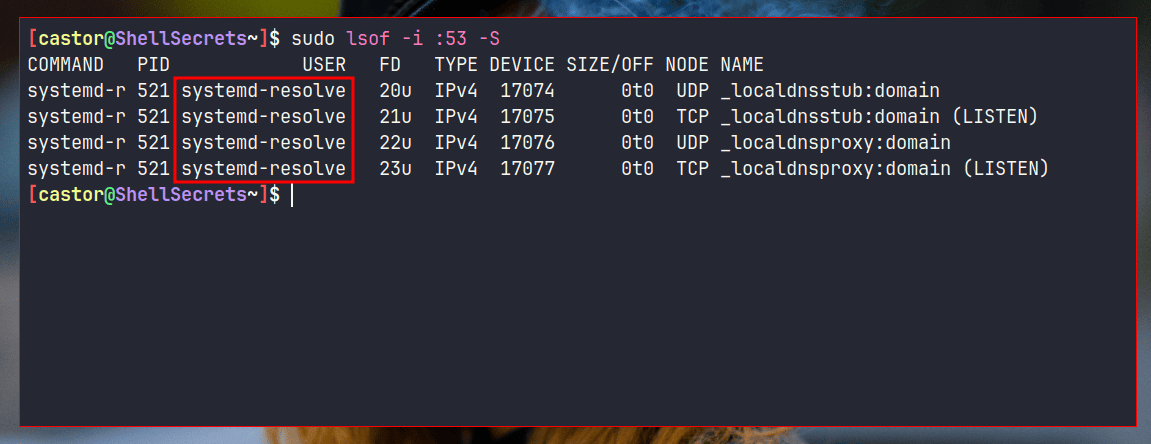
As seen from the screenshot above, the service listening on the DNS port 53 is systemd-resolved. It could be dnsmasq, nscd or BIND as well.
- Based on the DNS Resolver your Linux system is using, use the following commands to clear the DNS cache in your system.
- systemd-resolved
sudo resolvectl flush-caches sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches- dnsmasq
sudo killall -HUP dnsmasq sudo systemctl restart dnsmasq- NSCD
sudo nscd -i hosts sudo systemctl restart nscd.service- BIND
sudo rndc flush - Restart your computer.
- The DNS cache is now clear.
Chrome and Chromium based browser
The Google Chrome and Chromium Based web browser maintains its own internal DNS cache. To clear it, follow these steps:
- Start Google Chrome or any other chrominum based browser.
- In the address bar, type the following command. The browser displays a list of hosts in its internal DNS cache.
chrome://net-internals/#dns
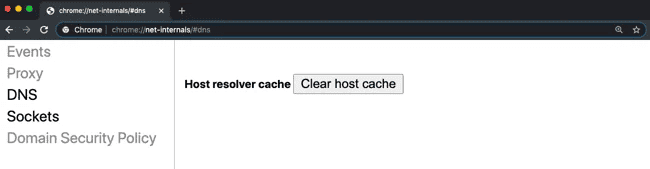
- Click Clear host cache.
- In the address bar, type the following command:
chrome://net-internals/#sockets
- Click Close idle sockets, and then click Flush socket pools.
- Restart your web browser.
Firefox and Firefox based browser
- Start Firefox or any other firefox based browser.
- Type the following commadn in the address bar:
about:networking#dns
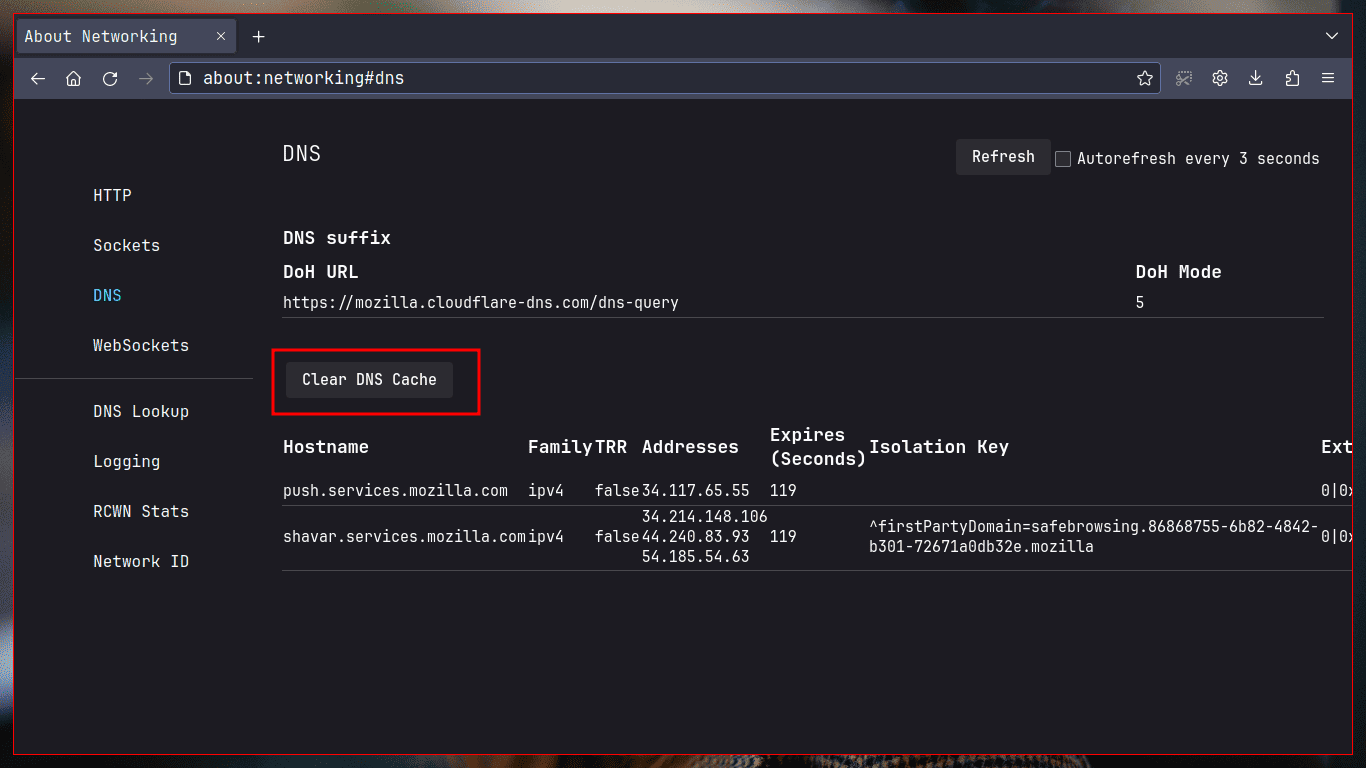
- Click the Clear DNS Cache button.
- Restart your web browser.